Which of These Describes the Rate of This Chemical Reaction
Inhibitors increase the rate of a reaction. Describe how the four major factors influence the rate of a chemical reaction.
Reactant Products A B change in number of moles of B Average rate change in time moles of B t A Rate t B t Since reactants go.

. Aims rationale why youthink the results will be important and hypotheses for your study. These exponents may be either integers or fractions and the sum of these exponents is known as the overall reaction order. A catalyst lowers activation energy increasing reaction rate.
Effect of Temperature on Reaction Rate 1. Increasing pressure increases reaction rate. The change in the concentration of a reactant or a product with time Ms.
Most chemical reactions occur very rapidly. Most chemical reactions occur at moderate rates. Increasing temperature increases reaction rate.
In a solution increasing the amount of reactants increases the reaction rate. The initial rate is faster than the rate later in time. It is expressed as The half-life of a reaction t12 is the time it takes for the reactant concentration A to decrease by half.
These rates give the rate of reaction for the entire time interval Δt and hence are called average rates of reaction. A reaction can also be described in terms of the order of each reactant. Describe a research study in which we could make use of the dna we have collected inconjunction with habitat andor morphological traits.
Which of the following best describes the rates of chemical reaction. Reaction rates are therefore determined by measuring the time dependence of some property that can be related to. The rate of a chemical reaction.
Kinetics deals with how fast chemical reactions happen and with how these rates are dependent upon factors such as concentration temperature or the presence of a catalyst. Chemical reactions often involve color changes temperature changes gas production or precipitant formation. Which of following units can be used to describe the rate of a chemical reaction.
In the reaction 2HgO-2HgO2m we measure the evolution of gas to determine the rate of reaction. A concentration of reactants As the concentration of reactants increases the number of collisions per unit time ---Select--- increase decrease and the reaction rate ---Select--- increases decreases. Simple examples of everyday reactions include digestion combustion and cooking.
3 Increasing the pressure in gases. There are five general properties that can affect the rate of a reaction. Pour about 5 mL of 60 M HCl into each of three clean test tubes.
Choose the INCORRECT answer. Chemical reactions have a wide range of rates from extremely fast to extremely slow. Catalysts on the rates of chemical reactions and then explain these effects in terms of the collision theory.
Chemical Kinetics is the study of reaction rates how reaction rates change under varying conditions and by which mechanism the reaction proceeds. The more concentrated the faster the rate. Likewise the rate of a chemical reaction is a measure of how much reactant is consumed or how much product is produced by the reaction in a given amount of time.
After 15 minutes the colume of O2 us 035L. Chemical reactions are common in daily life but you may not recognize them. Review Constants Periodic Table For a first-order reaction the half-life is constant.
Chemistry questions and answers. B frequency factor The frequency factor is a measure of molecular. What are five ways you can increase the rate of chemical reaction.
What is the rate of reaction. The rate of a chemical reaction may be increased by. The concentration of the reactants.
Place one of the tubes in. Most chemical reactions occur very slowly. At the beginning of the reaction at 0 minutes 0020 L of O2 is present.
1 Increasing the temperature. This helps to speed up a reaction but does not take part in the chemical reaction. The above terms for the rate of disappearance of A and rate of appearance of B are average rates of reaction.
Look for signs of a reaction. Rate of reaction -12ΔNaΔt -ΔClΔt 12NaClΔt. It depends only on the rate constant k and not on the reactant concentration.
In this experiment we will examine the effect of the change of initial concentrations on the reaction rate of a colored dye crystal violet and hydroxide ion. The rate of a reaction is the change in concentration of the reactant or product divided by the change in timeTherefore the formula of rate of reaction for the above reaction would be. The amount of a substance in a given volume.
The presence of catalysts. In an endothermic reaction heat is Q. H 3 C 2.
The surface area of the reactants. Enzymes increase the rate of chemical. A usually is increased when the concentration of one of the reactants is increased B is dependent on temperature C may be increased by certain catalytic agents D will be very rapid if the activation energy is large E describes the change in concentration of a reactant or product.
The rate of reaction is the change in the amount of a reactant or product per unit time. At the beginning of the reaction at 0 minutes 0020 L of O2 is present. After 15 minutes the volume of O2 is 035 L.
2 Increasing the concentration in solution. Therefore Rate of Reaction Δ A Δ t Δ B Δ t. There are 5 ways to increase the rate of a reaction.
The rate of any chemical reaction is dependent on a host of factors which include. 4 Increasing the surface area of a solid. Enzyme function is independent of a physical and chemical environment factors such as pH and temperature.
Gases react more readily than liquids which react more readily than solids. The statement that is true about chemical reactions rates would be the capacity of reaction rates to change based on certain factors. The correct option would be C.
In the reaction 2HgO s 2Hg l O2 g we measure the evolution of gas to determine the rate of reaction. Catalysts speed up the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy. The temperature of the reaction.
Describe the methodsused to obtain the dna sequences and the possible analyses that can be done. To reiterate the exponents x and y are not derived from the balanced chemical equation and the rate law of a reaction must be determined experimentally. Factors that affect the rate of a reaction.
Enzymes increase the rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy barriers.

The Rate Law Concentration And Time Boundless Chemistry
What Are The Units Of Rate Of Reaction In Chemistry Quora

Temperature And Rate Of A Chemical Reaction Chapter 6 Chemical Change Middle School Chemistry
Chemistry Module 5 Types Of Chemical Reactions Http Www Youtube Com Watch V Aawccqb75d0 Single
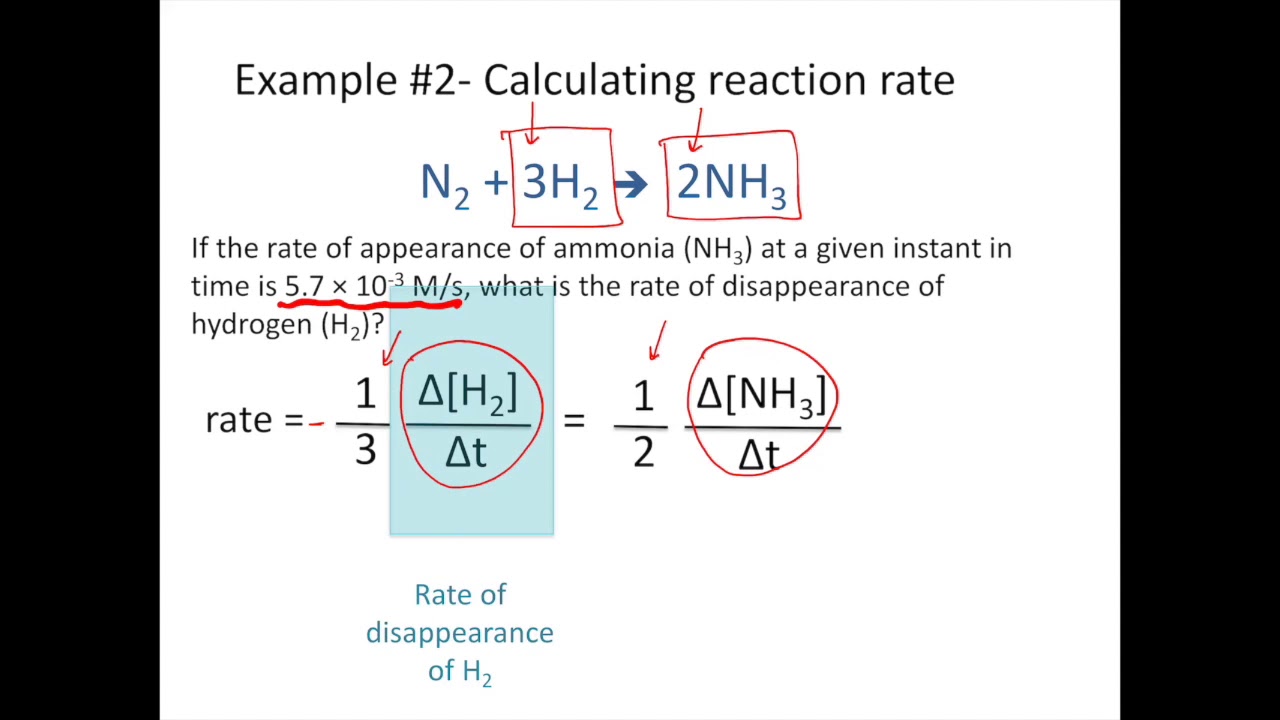
Chemical Reaction Rates Chemistry For Majors

Reaction Orders And Rate Laws Teaching Chemistry High School Chemistry Ap Chem

Glow Stick Lab Rate Of Reactions Next Generation Science Standards Glow Sticks 7th Grade Science

Lesson Explainer Factors Affecting Rate Nagwa

Metabolism Is A Term That Describes All The Chemical Reactions In Your Body These Chemical Reactions Keep Your High Metabolism Metabolism Booster Metabolism

Printable Posters Of Physical Science National Standards A Modern Design To Decorate Your Science Classro Physical Science National Standards Modern Classroom
Chemical Reaction Rates Chemistry For Majors

Kirstie Parker On Twitter Order Of Reaction Ozone Depletion Collision Theory

Enzymes And Temperature Guided Notes Worksheets Editable Enzymes Activity Guided Notes Enzymes
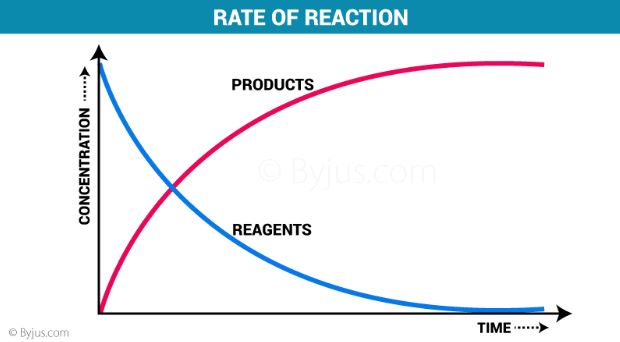
Rate Of Reaction Definition And Factors Affecting Reaction Rate

Factors Affecting Reaction Rates

Chemical Reaction Lab Chemical Reactions Scientific Skills Middle School Science

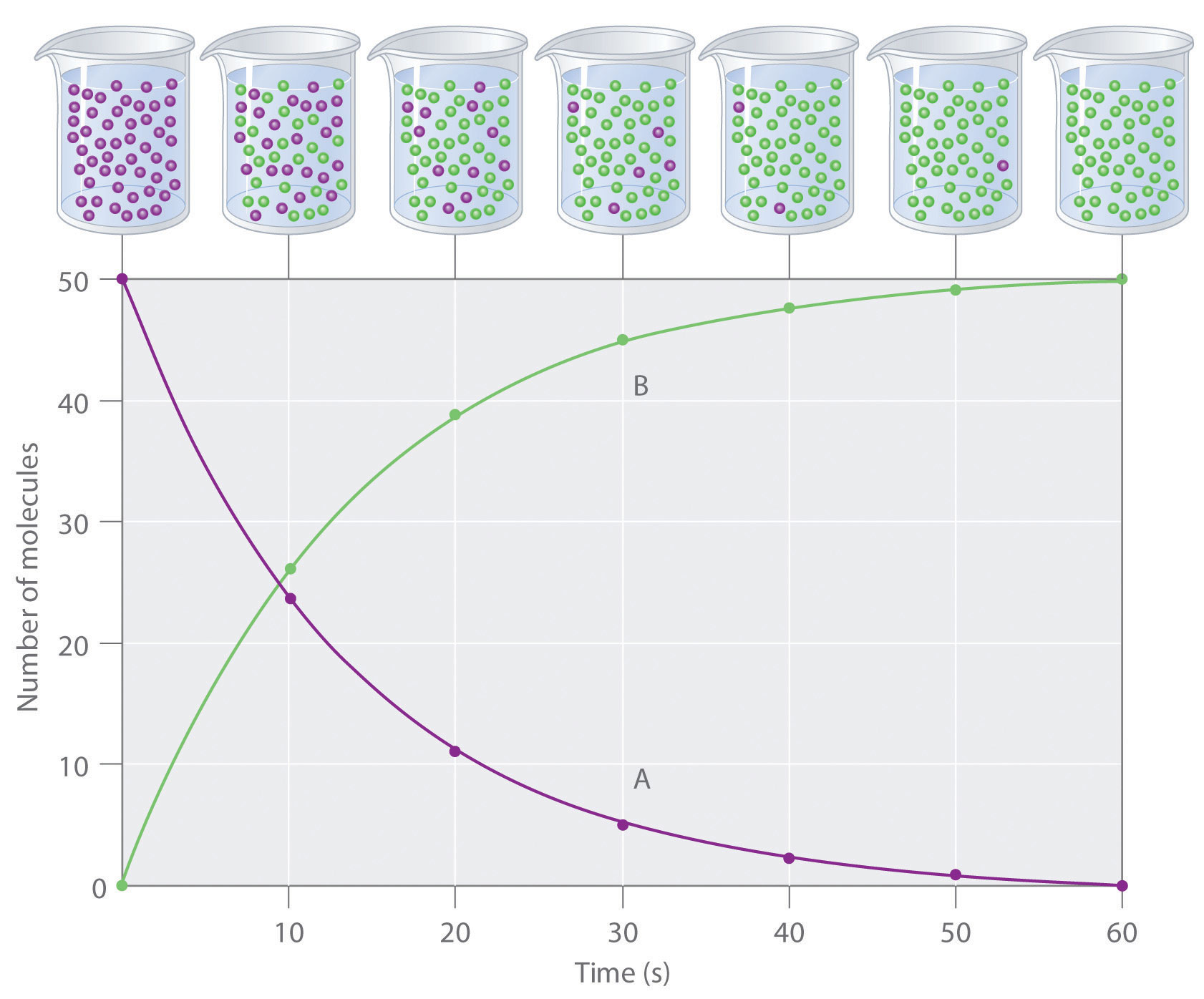

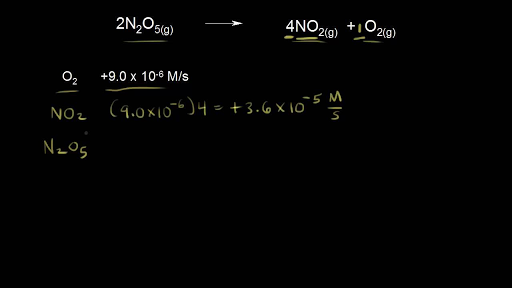
Comments
Post a Comment